Electrification in the Southwest Power Pool
In a detailed study commissioned by the Southwest Power Pool (SPP), Evolved Energy Research analyzed the potential impacts of electricity demand growth across sectors.

Introduction
The energy landscape is rapidly transforming with growing electricity demand one of the primary forces driving a new paradigm in resource planning. In a detailed study commissioned by the Southwest Power Pool (SPP), Evolved Energy Research analyzed possible load growth scenarios across sectors. This report offers critical insights into how demand in the region may evolve and is being used in further study by SPP to understand the implications.
Methodology
To execute this project, Evolved Energy Research employed its EnergyPATHWAYS model, a bottom-up stock rollover tool designed to project future energy demand across sectors with hourly fidelity. The study incorporated comprehensive data analysis, including historical electricity load patterns and weather conditions, to model SPP-specific Scenarios. Advanced machine learning techniques, such as random forest regression, were used to develop granular load shapes, while spatial disaggregation methodologies ensured precise alignment with SPP's pricing zones. Additionally, EER’s expertise in integrating unconventional loads, such as hydrogen electrolysis and data centers, enabled the team to highlight the implications of emerging technologies. The result was a highly detailed assessment tailored to inform SPP’s long-term planning efforts.
Numbers to Know
Exploring the Electrification Scenarios
The report evaluates three electrification Scenarios, each reflecting varying levels of electricity adoption and infrastructure adaptation:
- Baseline Electrification: Represents a business-as-usual model with limited technological uptake.
- Moderate Electrification: Envisions moderate adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and other electrification technologies, leading to gradual increases in demand.
- Full Electrification: Assumes aggressive electrification across residential, commercial, industrial, and transportation sectors, creating profound changes in energy consumption patterns.
SPP Electricity Demand
Key Technical Findings
1. Electrification of Transportation.
Transportation electrification emerged as a key driver of increased energy demand across all Scenarios:
- Even under moderate adoption, EVs will significantly alter load profiles, particularly during peak charging periods.
- By 2050, transportation could account for nearly a quarter of electricity demand under the Full Electrification Scenario.
- Grid operators will need to plan for flexible demand-side management and
infrastructure upgrades to handle the increased load.
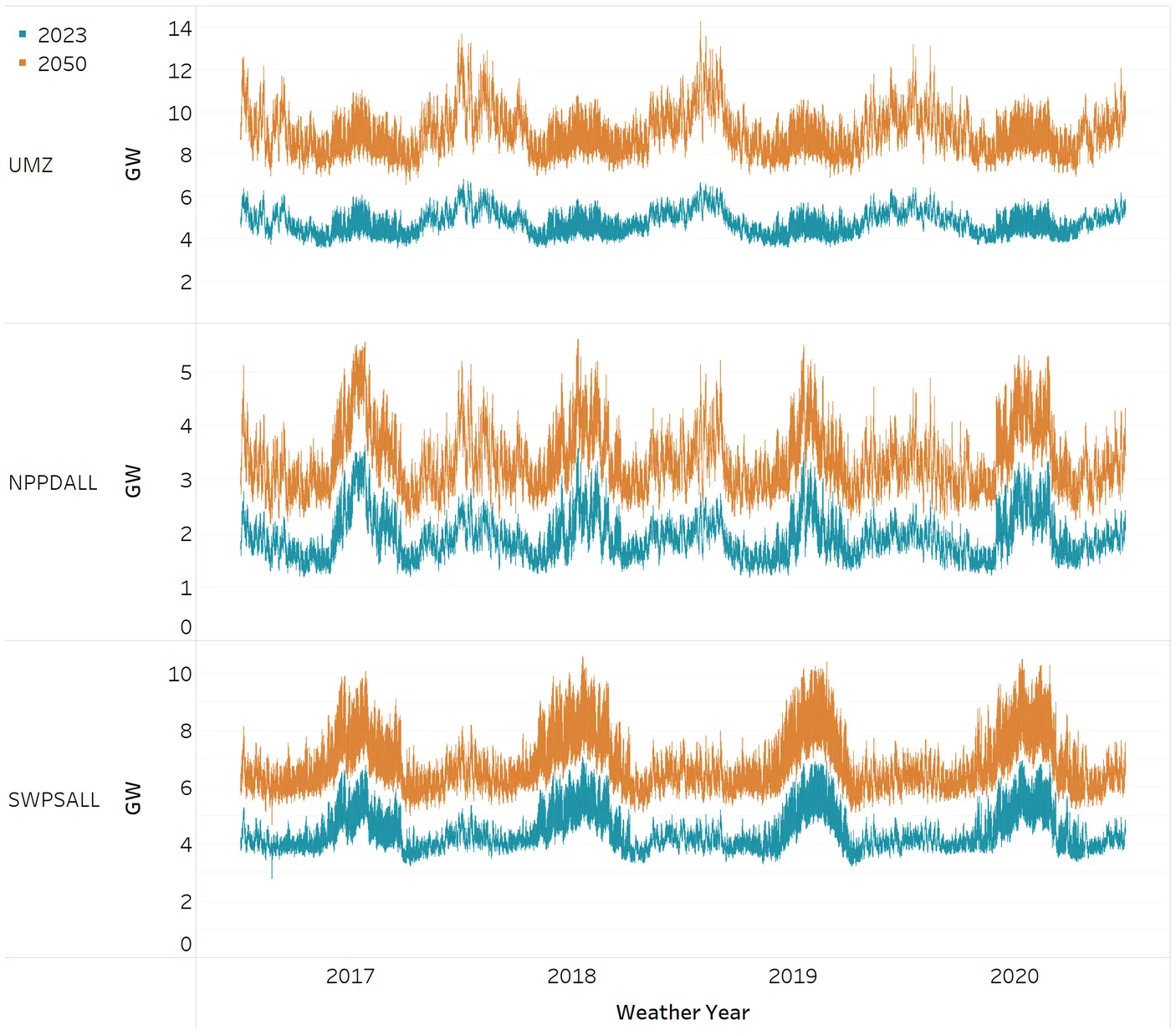
2. Seasonal Demand Peaks.
Electrification of heating technologies introduces significant seasonal variations:
- Northern regions may experience a shift to winter-peaking systems due to increased demand for space heating.
- Southern regions are expected to maintain summer-peaking profiles, with some areas potentially transitioning to dual peaks.
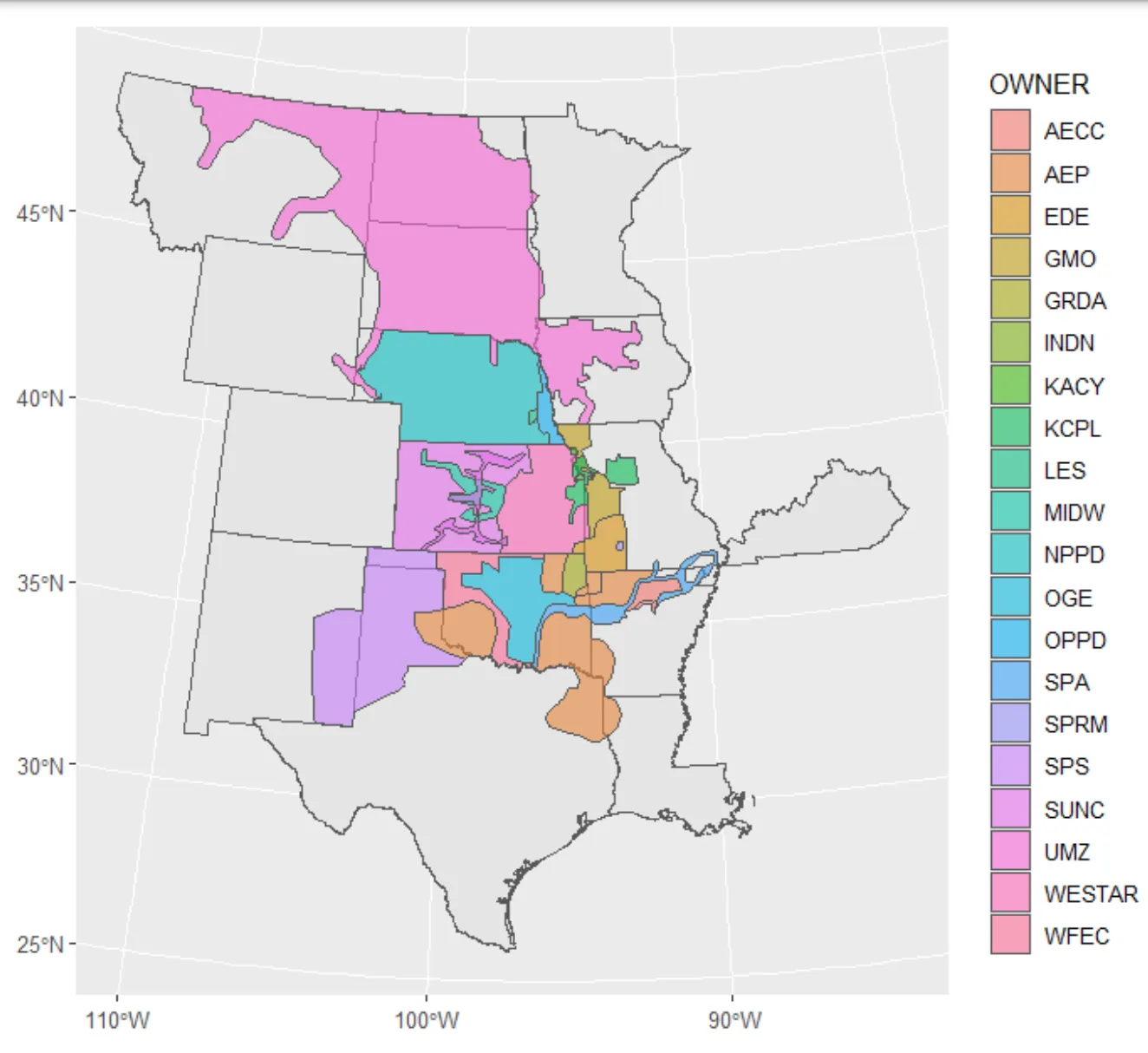
SPP Territory Map
North/South Full Electrification Load Comparison (w/o electrolysis load)
3. Unconventional Loads.
The emergence of unconventional loads, such as data centers and hydrogen electrolysis, adds complexity to grid management:
- Data Centers: Driven by AI, cloud computing, and digital services, data centers represent a rapidly growing source of electricity demand. Their locational flexibility, combined with the SPP region’s low-cost renewable resources, makes it likely for SPP to experience a growing share of load from data centers.
- Hydrogen Electrolysis: Hydrogen electrolysis has the potential to consume large amounts of electricity and compete for renewable resources, particularly wind energy, further complicating energy planning.
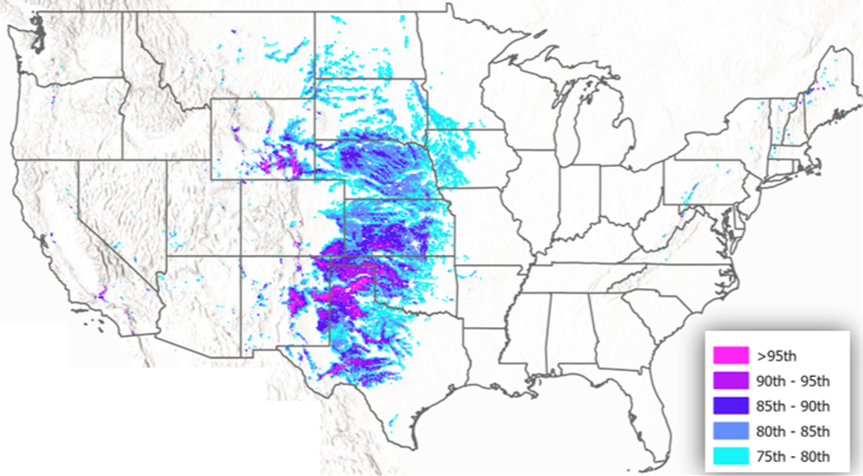
Cost Percentiles for E-Fuel Production